Environmental protection and underground storage activity
UGS activity is carried out in accordance with the applicable provisions of law in the environment friendly manner.UGS activity is monitored for the sake of environmental safety both in respect of devices and any possible emissions, in particular, the emission of methane from underground and aboveground parts of a storage facility.
In accordance with the Act on Environmental Protection of November 9th, 2010, every storage project requires a decision regarding environmental conditions, approval for the project implementation preceded by the conduction of environmental impact assessment procedure. The authority competent to issue a decision on the environmental permit for the project is a local, public administrative body (voyt, mayor) of the municipality in which the investment is located.
Following the submission of the application (along with the report), an institution initiating the proceedings for the assessment of environmental impact should make a public announcement regarding the submission of such application and the possibility for the community to make comments. Before issuing the above mentioned decision on the environmental permit for the project, the institution conducting the proceeding shall agree on the requirements for the project implementation with the Ministry of Environment, the relevant voivode and the State Provincial Sanitary Inspector (Państwowy Wojewódzki Inspektor Sanitarny).
Applying the above procedure provides high environmental standards and care for local communities.The examples of environmental protection measures for underground gas storage facilities created in partially depleted deposits and salt caverns
For the sake of environmental protection the following actions are monitored:
- surface protection – the observation of the subsidence based on a calculations of the spatial range of impact of geological structures used for natural gas storage
- protection of soil and surface waters - protection of soil and surface waters from the contamination, monitoring the quality of water and soil air,
- groundwater protection – the protection of individual geological layers from the contamination by the use of a properly designed and well cemented technical column of pipes,
- air protection - continuous monitoring of emissions from process equipment and greenhouse gas emissions,
- the protection against noise and vibration – the continuous monitoring of noise and vibration level of the identified sources,
- the protection of marine waters (in the case of UGS construction in salt caverns in close proximity to the sea) - monitoring the impact of brine solution discharged into marine waters.
The purpose of the environmental monitoring is:
- the elimination of potential hazards in the quickest time possible,
- general assessment of the overall impact of storage facility operation on the environment, soil and aquiferous layers,
- developing methods of monitoring which are relevant from the environmental protection perspective,
- taking optimal actions in the event of any malfunction occurrence.
Natural Gas - blue fuel
Natural gas is a mixture of saturated hydrocarbons which are in a gaseous state at room temperature. The main component of natural gas is methane. Natural gas also includes small amounts of ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), nitrogen (N) and helium (He). Some types of natural gas include hydrogen sulphide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Natural gas has a lower density than air. It is odourless and colourless. The characteristic odour of natural gas at distribution networks is obtained in the process of odorizing, performed for the sake of increasing the degree of gas safety.
Prior to the transmission of gas produced from the fields, it is subject to treatment (removal of acid gases, mercury, higher hydrocarbons, dehydration, particulates, nitrogen, etc.).
Natural gas is used as fuel or as raw material in many chemical manufacturing processes, such as acetylene, hydrogen, carbon disulfide, paints, synthetic fibres, synthetic rubber, plastics and carbon black.
Natural gas is called blue fuel - the name comes from the colour of the flame produced during the process of gas combustion.
What are the practical advantages of natural gas?
Natural gas enables achieving very high energy efficiencies when compared to other energy carriers being fossil fuels.
Natural gas is easy to transport over long distances using the most widespread method, i.e. pipelines or as liquefied natural gas (LNG). The gas combustion process is easy to control and monitor with the possibility of its automation.
Currently, the following fuels are commonly used for the production of thermal energy:
- coal,
- heating oil,
- natural gas.
Compared with coal and heating oil, the combusted natural gas emits significantly less nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide being the main cause of the greenhouse effect.
As the chart below indicates, natural gas is the most environmentally friendly fuel.
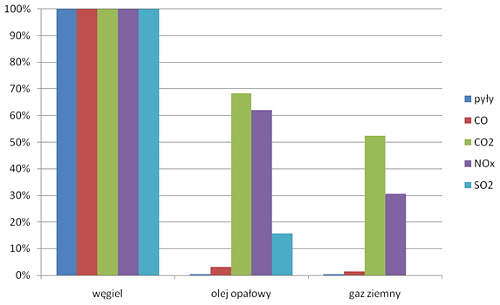
In Poland it is necessary to increase the share of natural gas in the production of electricity and heat because it is connected with the increase of the energy efficiency in manufacturing processes and the reduction of negative influence of emissions on the environment.